Content
- Starting
surfit - How to get results quickly
- Loading data
- Creating grid
- Gridding
- Saving results
- Visualizing results
Starting surfit
To start surfit you could run programm called surfit (surfit.exe under Windows). This program is extended Tcl shell application which automatically loads all surfit libraries. If surfit was installed correctly, you should see the following:
|
A common error received by first-time users is:
|
under Unix/Linux, or
|
under Windows. Here is solution for this problem:
Unix environment
This error is generated because the dynamic linker can't locate the libsurfit.so library. When shared libraries are loaded, the system normally only checks a few standard locations such as /usr/lib and /usr/local/lib. To fix this problem, there are several things you can do. First, you can set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable to include the directory with libsurfit library. If setting LD_LIBRARY_PATH, be aware that setting this variable can introduce a noticeable performance impact on all other applications that you run. To set it only for surfit, you might want to do this instead:
|
Finally, you can use a command such as ldconfig to add additional search paths to the default system configuration (this requires root access and you will need to read the man pages).
Windows environment
This error is generated because system can't locate the libsurfit.dll library. To fix this probelm you must set the PATH environment variable to the directory with libsurfit.dll:
(Windows 95/98/Me): The search path in Windows is normally specified in the autoexec.bat file, which is typically located in the root directory (c:). To add the surfit installation directory to your search path do the following from an MS-DOS Prompt Window:
- Type the following:
edit c:\autoexec.bat
- The contents of your autoexec.bat file will appear in a text editor. Find the line in your autoexec.bat that looks similar to the following:
PATH C:\DOS;C:\WINDOWS;C:\NETWORK;C:\NAV
- At the end of this line add the following:
;"c:\program files\surfit-3.0\bin"This assumes that you have installed surfit (libsurfit.dll) in the c:\program files\surfit-3.0\bin directory. If you have installed it in another directory, verify that you have entered an appropriate path. The leading semicolon is only necessary if there is not already a semicolon specified at the end of the "PATH" line.
- Press Alt+F+X. You will be prompted to save the file before exiting. Enter Y.
- Close any open applications and restart your PC. You may now access libsurfit.dll from any directory without specifying a path. An alternative to steps 2 and 3 above is to add the following line at the end of your autoexec.bat file: SET PATH = "C:\program files\surfit\bin";PATH%
(Windows NT/Windows 2000):
- Close any open MS-DOS Prompt Windows.
- Select Settings | Control Panel from the Start Menu.
- In the Control Panel, double click the System icon. The System (Properties) dialog appears.
- Select the Environment Tab.
- Select the PATH variable in the System (Environment) Variables or User (Environment) Variables boxes. If you are unable to locate the PATH variable, enter the following in the Variable box:
path
Enter something similar to the following in the Value box:
"c:\program files\surfit-3.0\bin"
How to get results quickly
This way is useful for most common task: interpolation of scattered data points or for contours approximation.
You will need only 3 commands: file_load, surfit and file_save. Also you may want to use surf_plot command to get results in PostScript file.
|
First commands loads your data from my_data.txt file. It recognizes most of file format and data types supported by surfit. Second command runs surfit gridding algorithm. Also it automatically creates so called "gridding rules" for loaded data and creates grid for that data. Third commad saves all data in memory with the surface obtained after gridding into "my_results.dat" file. Last commands plots resulting surface into PostScript file.
Loading data to surfit
To examine data, already loaded use mem_info command.
Automatic file loading
There is file_load command that tries to recognize file format and load it into surfit memory.
loading points
The pnts_read command reads formatted text files containing scattered data points coordinates. Text file should be organized as a rectangular table of numbers, separated by blanks, with one row per line, and an equal number of elements in each row. For example, outside of surfit, create a text file containing these four lines:
|
Store the file under the name points.txt Then the command
|
reads the file and creates the points dataset. This dataset contains 4 points with X,Y and Z coordinates placed in first, second and third columns. If points.txt consists of only 3 columns:
|
then the command arguments can be truncated:
|
You can get some info about points datasets with following commands:
|
Here you can browse all commands for points.
loading curves
surfit supports several types of curves:
| curve | 2D piecewise linear curve | |
| area | polygonal region | |
| contour | 3D piecewise linear curve |
The curves reading commands read formatted text files containing coordinates of curve nodes. The text file should organized as a rectangular table of numbers, separated by blanks, with one row per line, and an equal number of elements in each row. For example, outside of surfit, create a text file curve.txt containing these lines:
|
To read curve from file curve.txt use command:
|
loading surfaces
surfaces can be loaded from Surfer GRD-ASCII and surfit datafile format. To load surface from Surfer GRD-ASCII file use the command:
|
To load surface from surfit datafile use the command:
|
Here you can browse all commands for surfaces.
Creating grid
surfit uses equdistant grid for gridding procedures. This grid can be described with only 6 parameters:
- X-coordinate of the first node of the grid
- X-coordinate of the last node of the grid
- cell size in X-direction
- Y-coordinate of the first node of the grid
- Y-coordinate of the last node of the grid
- cell size in Y-direction
You can create grid object with grid_get command. For example, command
|
In most cases you can use grid command with only 2 parameters to specify cell sizes:
|
surfit automatically produces grid with cells of specified size. This grid will cover all data objects, loaded into memory.
Gridding
Gridding methods produce a regularly spaced, rectangular array of Z values from regularly and irregularly spaced XYZ data. The term "irregularly spaced" means that the points follow no particular pattern over the extent of the map, so there are many "holes" where data are missing. Gridding fills in these holes by extrapolating or interpolating Z values at those locations where no data exists.
For each data, loaded into surfit memory you can specify gridding rule, which describes how to use your data in surfit gridding algorithm.
Gridding procedure consists of 4 steps:
- load data into memory
- create grid
- create ordered set of gridding rules
- execute surfit gridding algorithm
Here is some examples:
<UL>
<LI>
<a href="points__exact_8tcl-example.html">Interpolation of scattered data points</a>
<LI>
<a href="trend_8tcl-example.html">Interpolation of scattered data points with trend and fault</a>
<LI>
<a href="points__approx_8tcl-example.html">Approximation of scattered data points</a>
<LI>
<a href="curve_8tcl-example.html">Interpolation/approximation of curves with constant values</a>
<LI>
<a href="contour_8tcl-example.html">Interpolation/approximation of contours</a>
<LI>
<a href="area_8tcl-example.html">Interpolation/approximation of areas</a>
<LI>
<a href="surface_8tcl-example.html">Interpolation of surface</a>
<LI>
<a href="surface__add_8tcl-example.html">Approximation of surface</a>
</LI>
</UL>
Saving results
After gridding procedure result saves as new surface named with map_name variable value. You can export it to Surfer GRD-ASCII format with command surf_save_grd or to surfit datafile with command surf_save. Also you can save your results into surfit datafile with all other data in memory with command file_save.
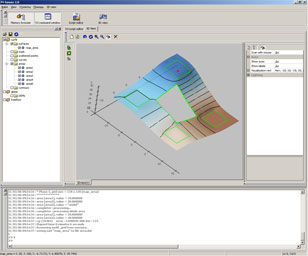
Visualising results
The simplest way to visualise your results is to use funner program. This program can be founded here: www.gridding.info. funner accepts both Surfer GRD-ASCII and surfit datafiles.
Funner window screenshot
Also you can select file from command line:
|